4.6 Example 1
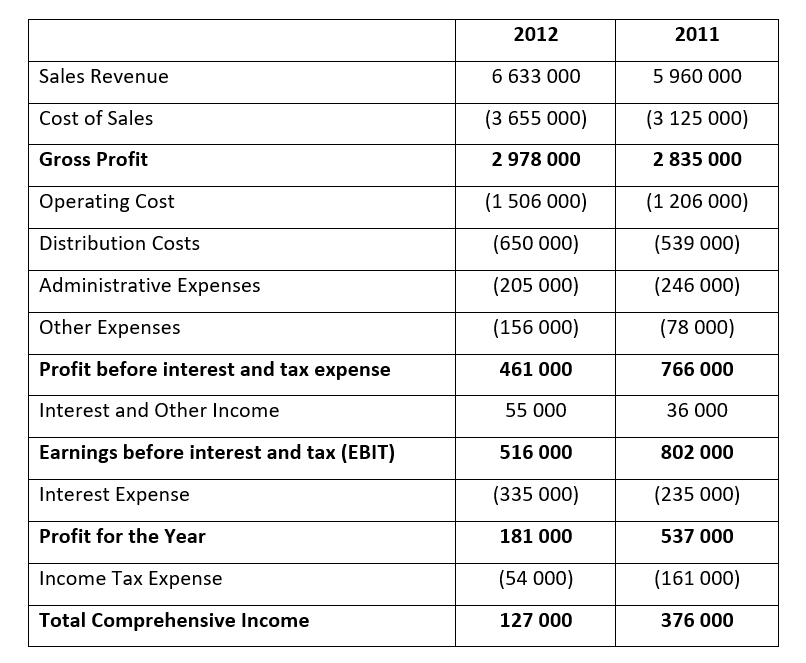
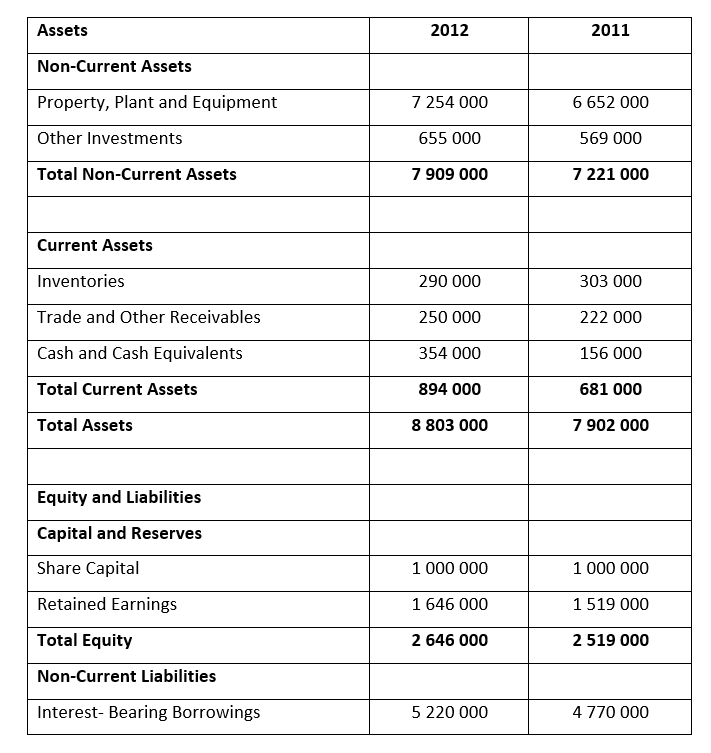
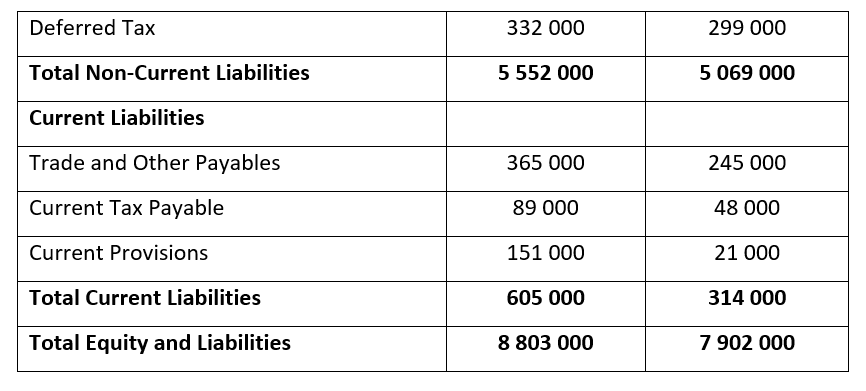
- Roc Limited has 5 000 000 authorised shares, 1 000 000 have been issued
- Assume that 100% of ordinary shares were recently valued at R3 000 000 (2011: R2 800 000) and that the market value of all liabilities equals the carrying value for both years
- The market value of each share after the release of these audited financial statements were 300 cents (2011: 280 cents)
- The dividend per share is 6 cents (2011: 5 cents)
- The opening balances of inventory for 2011 was R79 000
- The opening balance of capital and reserves for 2011 was R2 350 000 and for total assets it was R7 530 000
- The amount of sales on credit is 60% of revenue for both years
- Actual purchases made by Roc Limited on credit were R3 642 000 (2012) and R3 349 000 (2011)
- Value-Added-Tax (VAT) is calculated at a rate of 14%
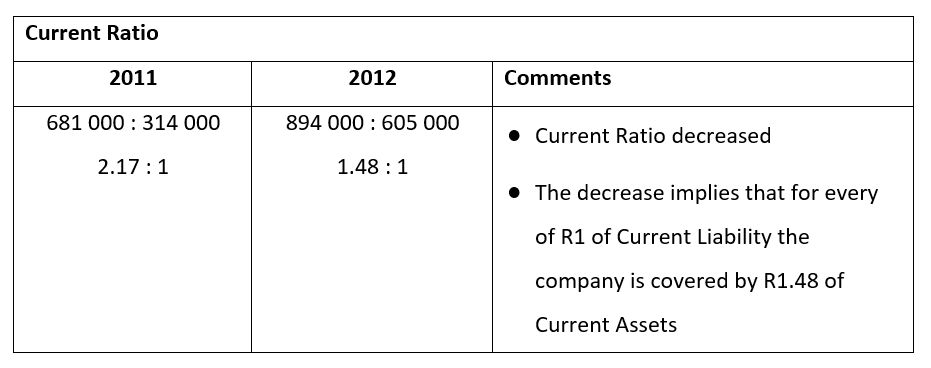
As can be seen above the current ratio is the value of the current assets as expressed as a ratio to the current liabilities. The ratio is obtained by dividing both number by the smallest number as is the case in 2011 by 314 000 and in 2012 by 605 00. The resulting answer means that for every R2.17 held in current assets the business owes R1 in current debt or liabilities.
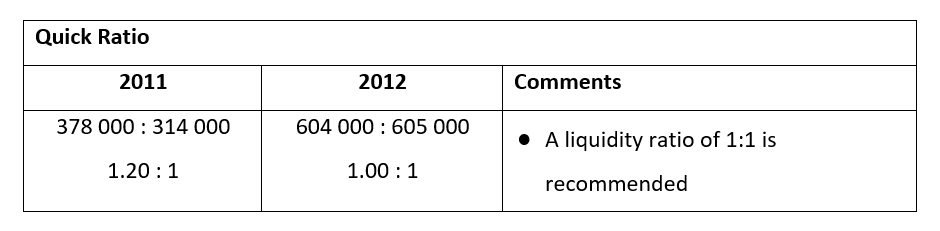
The quick ratio or acid test ratio uses the current assets amount of the current ration but deducts the value of stock and then again, this value is compared to the value of current liabilities and the results are as follows: for every R1.20 held in current assets which can be easily liquidated into cash the business owes R1 in current liabilities for the year 2011 and for the year 2012 the amount is R1 for each.

Tasks
Having understood the above, apply yourself in answering the following for the two respective years:
- Inventory Days
- Receivable days
- Payable days
- Cash conversion cycle
- Debt to equity ratio
- Debt ratio
- Earnings per share
- Dividend per share
- Return on capital
- Gross profit margin
- Net profit margin